TurboTides
Download PDFTurbomachinery Integrated Design System
TurboTides is a specialized tool tailored specifically for turbomachinery design, based on systems engineering principles, offering turbomachinery industry users an integrated, intelligent, and customizable CAE design solution.
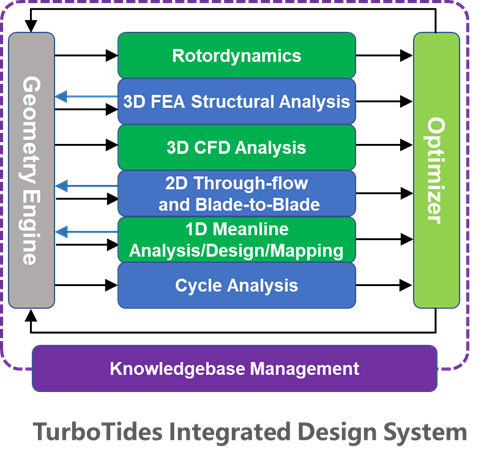
With support from its proprietary database, TurboTides integrates various functional modules centered around geometric modeling. These include system cycle analysis, one-dimensional mean-line design analysis, two-dimensional passage flow calculations, three-dimensional CFD calculations, three-dimensional FEA, fatigue life assessment, crack propagation analysis, and rotor dynamics analysis. Data seamlessly transfers between these modules, and they can all connect to the optimizer for automated design optimization.




MAIN FUNCTION
Cycle Modeling & Analysis
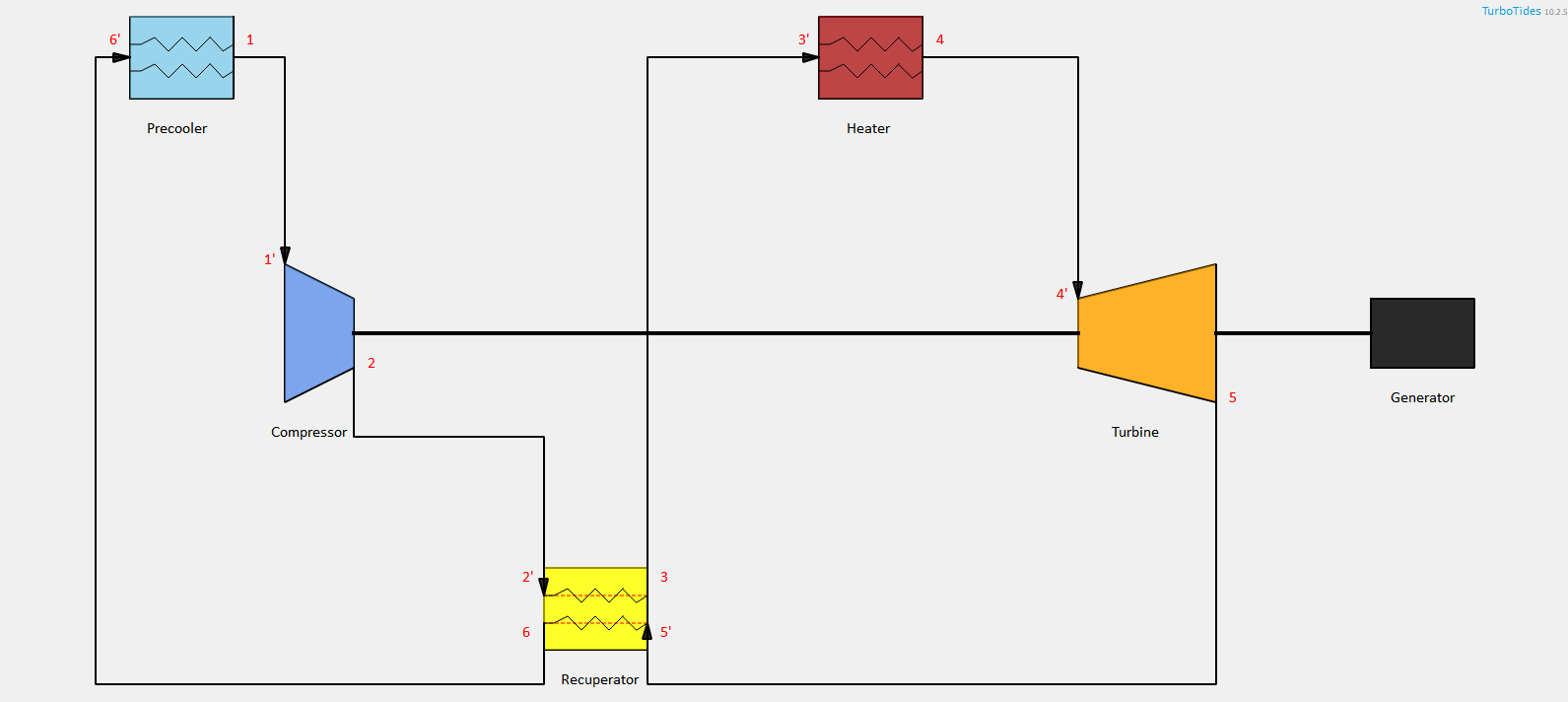
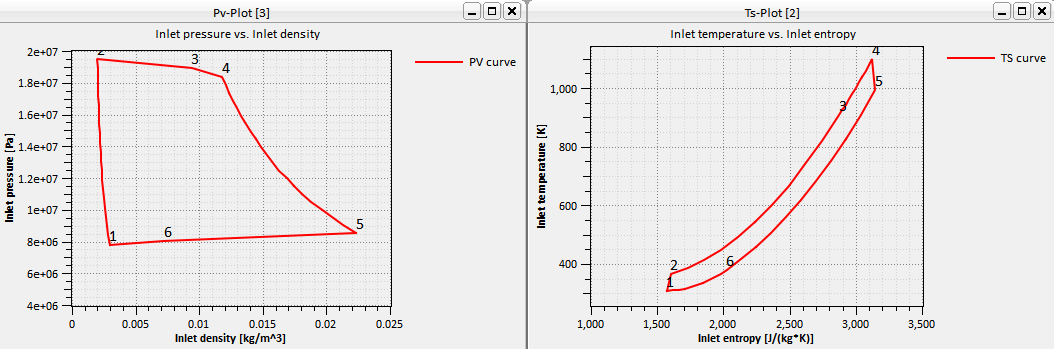
TurboTides cycle analysis supports the design and analysis of thermodynamic cycles in various layout forms.
- Rankine cycle& Organic Rankine Cycle (ORC)
- Gas turbine cycle
- Supercritical CO2 cycle
- Refrigeration Cycle
- Turbocharging Matching
- Multi-stage compression system design and analysis, including gear-type multi-stage compression (IGC)
- Supports power turbine model and turbojet engine model.
- Supports adding a secondary air system (SAS), modeling of turbine cooling and anti-surge flow path.
- Supports simulation of Printed Circuit Heat Exchangers (PCHE).
- Supports various options for compressor and turbine model types, suchas one-dimensional mean-line models and characteristic maps.
- With embedded optimizer, automatic optimization of cycle parameters can be achieved.
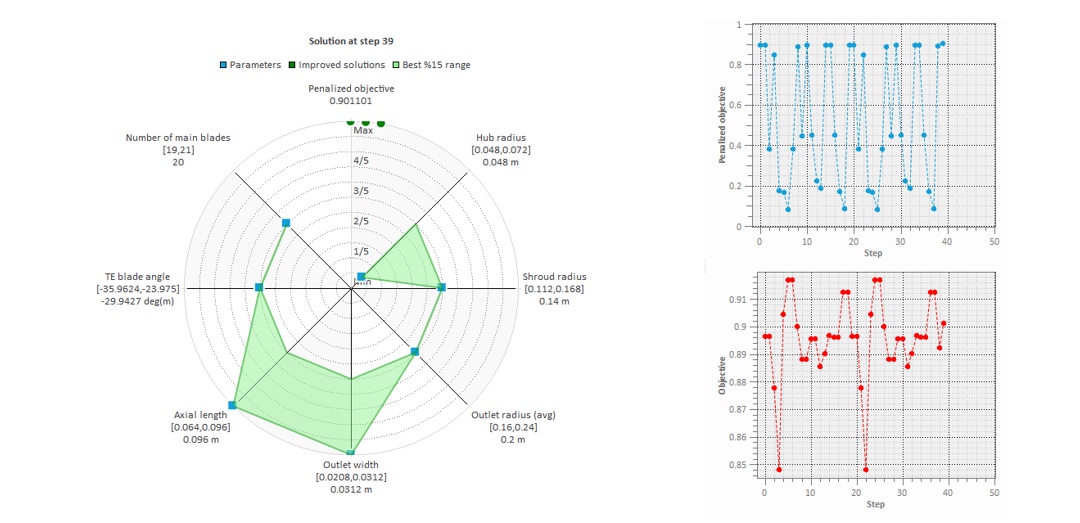
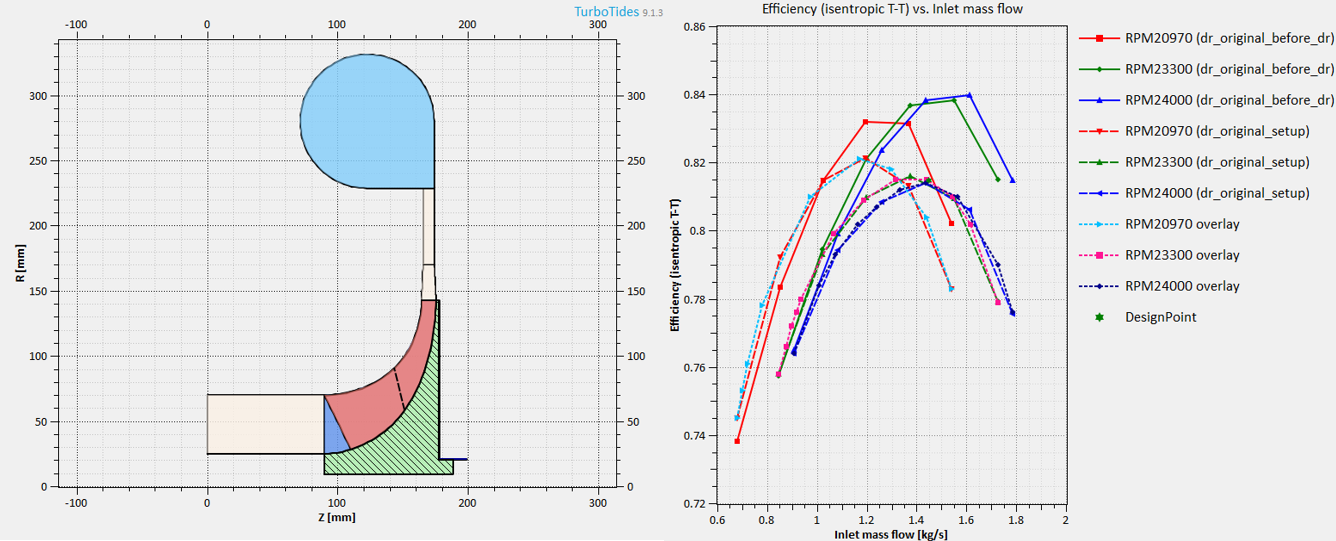
1D Meanline & Analysis Module
Supports preliminary design and analysis of radial, mixed-flow, and axial forms of compressors, turbines.
- Rapid design of centrifugal, axial, and mixed-flow pumps, incorporating design experience from the pump industry.
- Supports the design and analysis of counter rotating axial flow compressors.
- Based on REFPROP10 and fast lookup tables, it provides real-fluid models for two-phase flow calculations.
- Capable of modeling of components such as airfoil diffusers and tandem diffusers.
- Functionality includes scaling, cutting, flow cut, and variabe geometry models.
- Embedded optimizer with user-friendly operations supports optimization of parameters in the one-dimensional mean-line model.
- User Defined Functionality (UDF) allows users to change the default models and functionalities of the program.
* The Data Reduction function can calibrate the one-dimensional model to match experimental / simulation data point by point across the entire performance map. After calibration, the model can accurately predict machine performance curves when replacing working fluids or modeling similar designs.
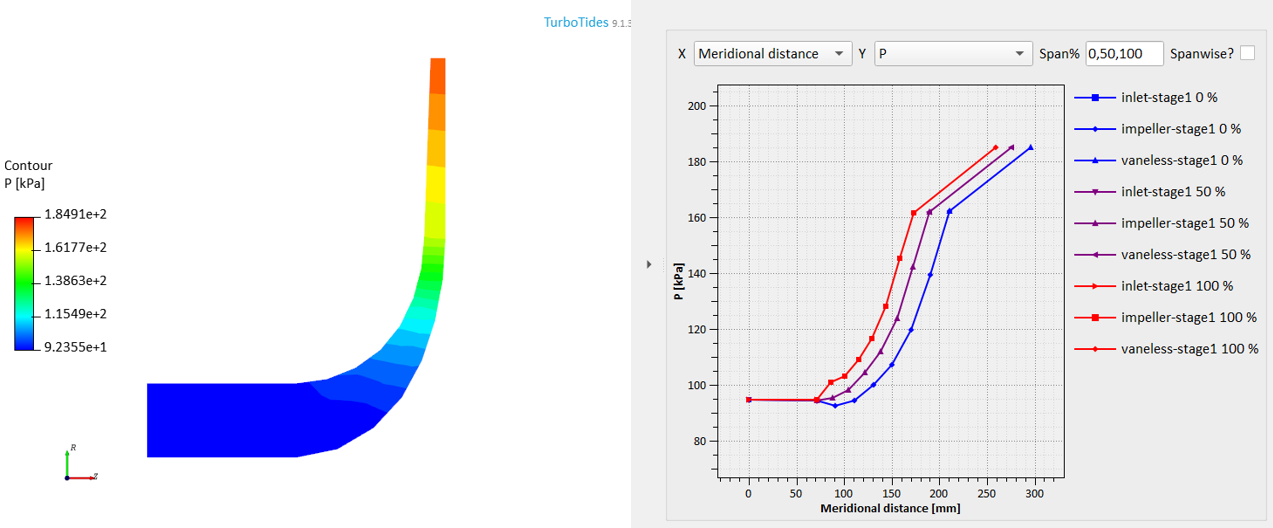
2D Through-Flow Analysis Module
Includes meridional (S2 surface) through-flow calculations and blade-to-blade (S1 surface) calculations
- Based on streamline curvature method.
- Automatically extract blade geometry (blade angle, thickness, lean angle).
- Generate grids automatically from 3D geometry.
- Consider loss models, deviation angle models, blockage models, and radial mixing.
- Supports flow passage and blade profile optimization, with convenient operation.
- Supports multi-operating point analysis function.
- Supports comparative design function, compare flow results under design and off design conditions.
- Supports post-processing plotting for individual components.
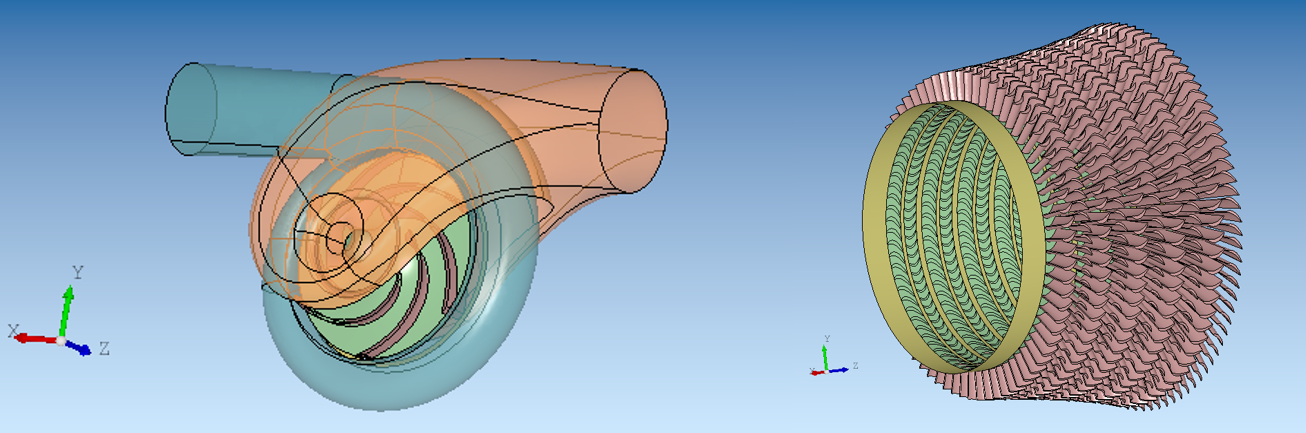
Geometric Modeling
The geometric modeling module comprehensively supports the generation of 3D parameterized geometric models.
- Encompasses the geometric configurations of common components found in centrifugal or axial compressors, turbines, pumps, and fans.
- Offers real-time visualization and geometric editing features, including adding/subtracting/editing adjustments to flow components, mechanical structure editing (such as hub shape, chamfering, filleting, and shaft holes), and impeller cutting and scaling functions.
- Supports various methods for defining parameters such as throat area in wedge diffusers.
- Capable of generating various airfoil blade models, such as NACA, DCA, and MCA.
- Robust volute editing features allow for easy control and editing of various cross-sections, tongue, outlet pipe sections, and double volute configurations.
- Supports parameterized modeling of fan inlet chambers, pump inlet chambers, and double-suction inlet chambers.
- Provides the capability to export three-dimensional models in a universal format for solid and fluid domains.
- Supports the import of existing 3D CAD models, which can be parameterized and used for simulation and optimization design.
- The embedded database facilitates the convenient storage and reuse of 3D component models.
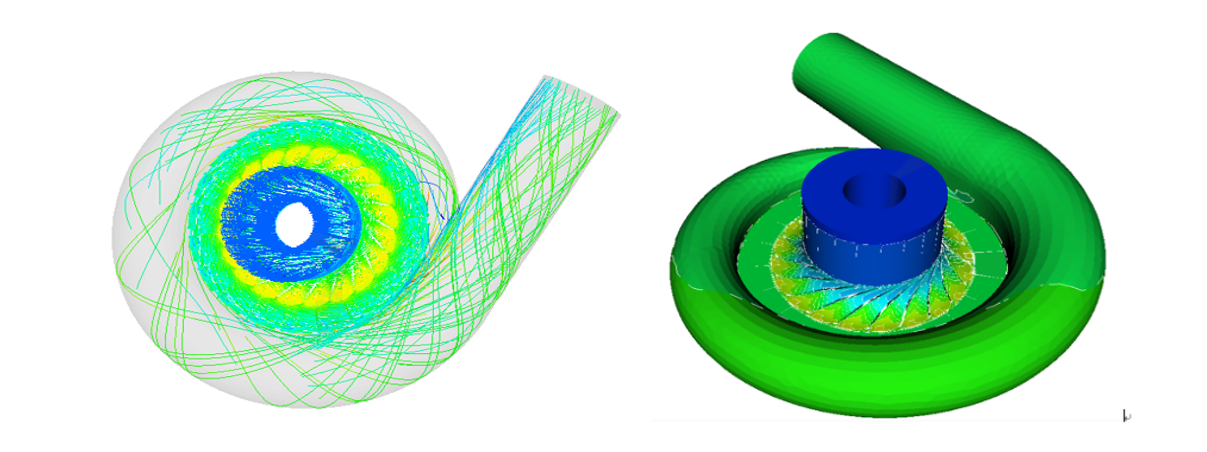
3D CFD Flow Field Simulation Analysis Module
The 3D CFD module provides a full 3D pressure-based flow field simulation solver that supports structured, unstructured, or hybrid grids.
- Supports parallel computing.
- Automatically generates grids and allows expert manual adjustment.
- Incorporates grid smoothing algorithms with added source terms to improve grid orthogonality.
- Allows the specification of boundary layer thickness or y+ values.
- Automatically sets boundary conditions and imports inlet/outlet boundary conditions and fluid properties from one-dimensional analyses.
- Calculates real-fluid properties and generates thermodynamic property tables.
- Supports simulation calculations for cavitation and two-phase flow.
- User-friendly post-processing features include text reports and views of grids, contours, vectors, streamlines, and isosurfaces.
- Facilitates easy comparison between results from three-dimensional CFD flow field analyses and predictions from the one-dimensional mean-line module.
- Provides an interface with the third-party software TurboGrid.
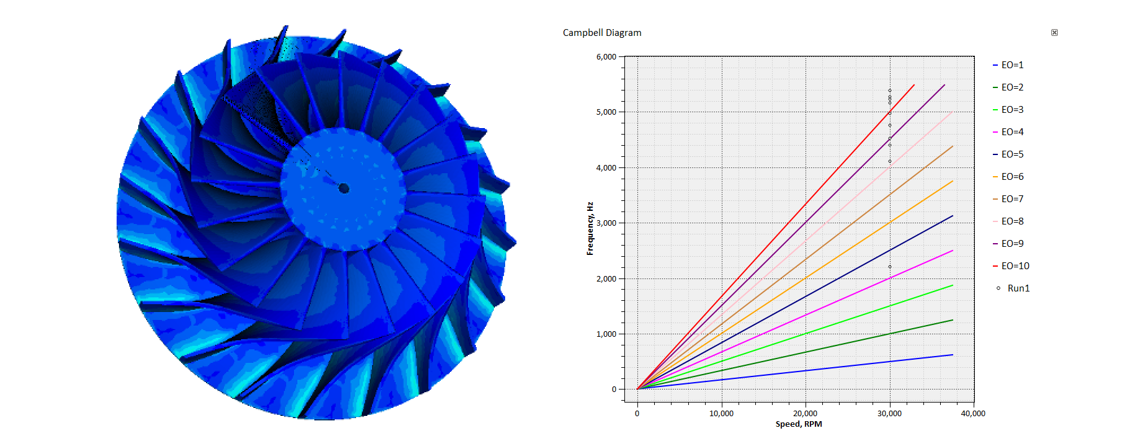
3D FEA Finite Element Module
Supports finite element analysis of impellers and volutes.
- Convenient pre-processing functions: automatic grid generation, automatic load and constraint settings with The 3D FEA finite element module.
- Supports one-way fluid-structure coupling with The 3D FEA finite element module.
- Supports calculations with linear and nonlinear materials, including elastic, plastic, creep, and hyperelastic materials.
- Provides functions for static strength analysis, thermal analysis, and modal vibration analysis.
- Supports harmonic response analysis, transient dynamics analysis, transient heat transfer analysis, and stochastic vibration analysis.
- Quickly calculates mass, moment of inertia, etc.
- User-friendly post-processing features include text reports, Campbell diagrams, interference diagrams, contour maps, and deformation diagrams.
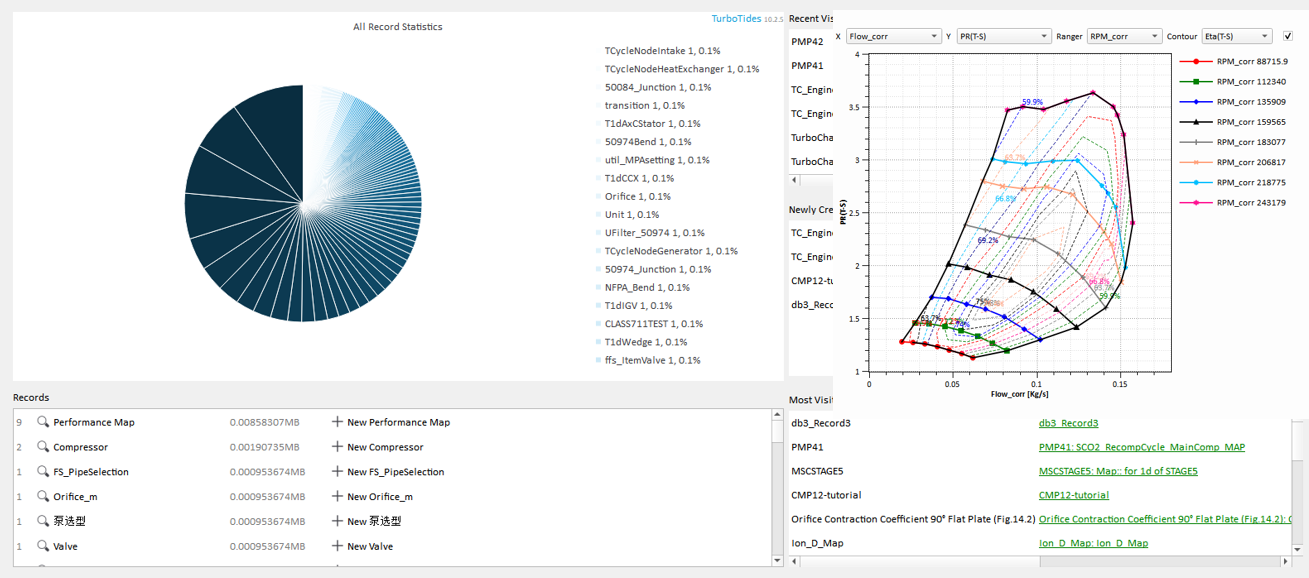
Embedded Database
The embedded database is a deployable data storage center accessible over the network, equipped with permission control functionalities, seamlessly interconnected with the design modules. Users can conveniently store and reuse existing design models, test data, geometric models, and custom functions through the database.
- Any object within TurboTides (components, machines, curves, fluid models, etc.) can be saved to the database and reloaded into the current design.
- The object-oriented database can input various complex data structures such as performance maps, components, machines, geometric models, and fluid models.
- Users can customize data record types and specify properties through scripts.
- All content stored in the database is searchable, recoverable, and reusable.
- Supports both local and remote online access to data.
Optimization Design
Both global /machine level optimization and local component level optimization can be performed using TurboTides' built-in optimization functionality. By setting optimization parameters, defining objectives, selecting appropriate solvers, and optionally constraining input and output parameters, users can conduct automated optimization calculations. The software provides a visualization interface during the optimization process to display real-time iterations of the optimization.
- Supports Latin Hypercube Sampling, grid-adaptive search, Maximum Expected Improvement algorithm, and Genetic Algorithm optimization algorithms.
- Provides the fourth-generation OASIS optimization algorithm based on artificial intelligence and machine learning, effectively addressing optimization design problems with high variability, expensive constraints, multiple objectives, and black-box constraints.
- The optimizer can call solvers for cycle analysis, one-dimensional, two-dimensional passage flow, CFD, and FEA either separately or in combination.
- Through script writing, users can customize complex optimization processes, such as multidisciplinary optimization involving CFD and FEA to optimize flow fields and impeller structures.